Understanding Blood Sugar Monitoring and Healthy Eating for Diabetes Management
Most people believe that all fruits are safe for a balanced diet, but for those focused on strict glucose management, some "healthy" choices can be misleading. Discover why three specific fruits might be causing unexpected spikes in your readings and how modern monitoring tools help you identify these triggers in real-time. Learn to make informed nutritional choices and stay within your target range every single day
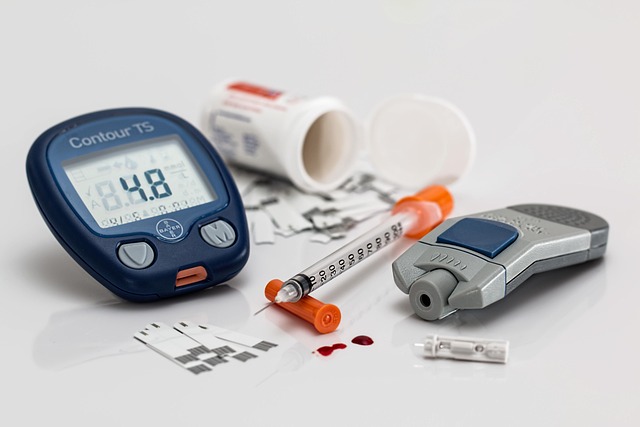
Managing diabetes effectively involves understanding the intricate relationship between blood sugar monitoring and nutritional choices. Modern diabetes care has evolved significantly, offering individuals sophisticated tools and evidence-based strategies to maintain optimal glucose control. The combination of advanced monitoring technology and informed dietary decisions creates a foundation for successful long-term diabetes management.
Proper diabetes management requires consistent attention to both immediate glucose readings and long-term dietary patterns. Healthcare professionals emphasize that successful diabetes control depends on understanding how different foods, activities, and monitoring techniques work together to influence blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Glycemic Load vs. Healthy Image: Understanding Food Impact
The concept of glycemic load provides a more comprehensive understanding of how foods affect blood sugar compared to simply focusing on glycemic index alone. Glycemic load considers both the quality and quantity of carbohydrates consumed, offering a more practical approach to meal planning. Foods with lower glycemic loads tend to produce more gradual increases in blood glucose levels.
Understanding glycemic load helps individuals make informed choices about portion sizes and food combinations. For example, combining high-fiber vegetables with moderate amounts of whole grains can significantly reduce the overall glycemic load of a meal. This approach allows for more flexibility in meal planning while maintaining better glucose control.
The visual appearance of healthy foods often correlates with their nutritional value and impact on blood sugar. Colorful vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains typically indicate nutrient-dense options that support stable glucose levels. Learning to identify these visual cues helps individuals make quick, informed decisions when shopping or dining out.
The Role of Advanced Monitoring Supplies in Diabetes Care
Modern diabetes monitoring supplies have revolutionized how individuals track and manage their glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time data, allowing for immediate adjustments to diet, medication, or activity levels. These devices offer insights into glucose patterns that traditional fingerstick meters cannot provide.
Advanced monitoring systems include features such as smartphone connectivity, trend arrows, and customizable alerts. These technological improvements help users identify patterns in their glucose levels and make proactive adjustments to their management strategies. The data collected can also be shared with healthcare providers for more personalized treatment recommendations.
Traditional blood glucose meters remain important tools in diabetes management, particularly for calibrating CGMs and making treatment decisions. Modern meters offer improved accuracy, smaller blood sample requirements, and faster results. Many devices now include memory functions and data management capabilities that help users track their progress over time.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Glucose Monitor | Dexcom G7 | $200-300 monthly |
| Traditional Blood Glucose Meter | OneTouch Verio | $15-30 for meter, $1-2 per test strip |
| Insulin Pen Needles | BD Ultra-Fine | $20-40 per box of 100 |
| Lancets | Accu-Chek FastClix | $15-25 per drum of 102 |
| Test Strips | FreeStyle Lite | $50-80 per box of 50 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Lifestyle-Driven Blood Sugar Stabilization Techniques
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in achieving and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles, leading to better overall glucose control. Even moderate exercise, such as walking after meals, can significantly impact post-meal glucose levels.
Meal timing and consistency contribute significantly to blood sugar stabilization. Eating meals at regular intervals helps prevent dramatic fluctuations in glucose levels throughout the day. Spacing meals appropriately and avoiding prolonged periods without food can help maintain more predictable glucose patterns.
Stress management techniques, including meditation, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep, directly impact blood sugar control. Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may interfere with insulin effectiveness. Incorporating stress-reduction strategies into daily routines supports overall diabetes management goals.
Hydration plays an often-overlooked role in blood sugar management. Proper hydration supports kidney function and helps maintain stable blood glucose levels. Dehydration can lead to concentrated glucose levels in the blood, making management more challenging.
Successful diabetes management requires integrating monitoring technology with lifestyle modifications and nutritional awareness. The combination of advanced monitoring supplies, understanding of glycemic load principles, and lifestyle-driven stabilization techniques creates a comprehensive approach to diabetes care. This integrated strategy empowers individuals to take control of their health while working closely with healthcare providers to achieve optimal outcomes. Regular monitoring, informed food choices, and consistent lifestyle habits form the foundation of effective diabetes management that can be sustained over the long term.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




