Pain management: how therapeutic massage eases neck, back & shoulder tension
Chronic tension in the neck, back, and shoulders affects millions of Canadians, often stemming from poor posture, repetitive strain, or stress. Therapeutic massage has emerged as a valuable approach for relief, offering targeted techniques that address muscle tightness and discomfort. By understanding how massage therapy works and which methods are most effective, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating this treatment into their wellness routine.
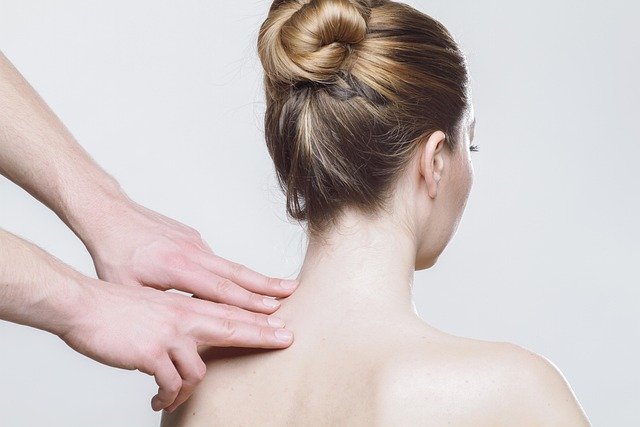
Therapeutic massage serves as a non-invasive option for managing persistent tension in common problem areas. Many Canadians experience daily discomfort due to desk work, physical labor, or stress-related muscle tightness. Massage therapy addresses these issues by improving circulation, reducing muscle stiffness, and promoting relaxation. Unlike temporary solutions, regular therapeutic sessions can provide lasting benefits when combined with proper self-care practices.
What types of therapeutic massage address neck, back, and shoulder tension?
Several massage modalities target relief, each with distinct approaches. Swedish massage uses long, flowing strokes to promote relaxation and improve blood flow, making it suitable for general tension. Deep tissue massage applies firmer pressure to reach deeper muscle layers, addressing chronic discomfort patterns. Sports massage focuses on areas stressed by athletic activity, while remedial massage targets specific injuries or conditions. Each type serves different needs, and practitioners often combine techniques based on individual tension patterns and treatment goals.
How do myofascial release and trigger point therapy work?
Myofascial release focuses on the fascia, the connective tissue surrounding muscles and organs. When fascia becomes tight or restricted, it can cause discomfort and limit movement. Therapists apply sustained pressure to these areas, allowing the tissue to soften and lengthen. This technique proves particularly effective for chronic tension conditions and postural issues.
Trigger point therapy addresses specific areas of muscle tension that refer discomfort to other body parts. These trigger points feel like small knots within muscle tissue. Therapists apply direct pressure to these points, holding until the muscle releases. Common trigger point locations include the upper trapezius for shoulder tension, the levator scapulae for neck discomfort, and the erector spinae muscles along the spine for back tightness. Both techniques require skilled practitioners who understand anatomy and can identify problem areas accurately.
Which areas benefit most from therapeutic massage?
The neck, back, and shoulders form an interconnected system where tension in one area often affects the others. The cervical spine and surrounding muscles bear the weight of the head, making the neck vulnerable to strain from forward head posture common in computer work. The upper back, particularly between the shoulder blades, accumulates tension from rounded shoulders and stress. The shoulder girdle itself involves complex muscle groups that stabilize and move the arms, often becoming overworked in repetitive tasks.
Therapeutic massage addresses these areas through systematic work on muscle groups. For neck discomfort, therapists focus on the sternocleidomastoid, scalenes, and suboccipital muscles. Back treatments target the trapezius, rhomboids, and paraspinal muscles. Shoulder work includes the rotator cuff muscles, deltoids, and pectorals. Understanding these target areas helps individuals communicate their needs effectively during sessions.
What safety considerations apply to therapeutic massage?
While generally safe, therapeutic massage has contraindications and precautions. Individuals should avoid massage over areas with acute injuries, infections, or skin conditions. Those with certain medical conditions including deep vein thrombosis, severe osteoporosis, or bleeding disorders should consult healthcare providers before treatment. Pregnancy requires specialized prenatal massage techniques.
During sessions, communication with the therapist remains essential. Discomfort levels should stay within a tolerable range, typically described as therapeutic rather than sharp or unbearable. Bruising occasionally occurs with deep tissue work but should not be excessive. Qualified massage therapists in Canada complete recognized training programs and may hold certification through provincial regulatory bodies, ensuring they understand anatomy, physiology, and safe practice standards.
How often should someone receive therapeutic massage sessions?
Session frequency depends on tension severity, individual response, and treatment goals. For acute discomfort or specific issues, weekly sessions for four to six weeks often provide initial relief. Chronic conditions may benefit from bi-weekly treatments over longer periods. Once symptoms improve, monthly maintenance sessions help prevent recurrence.
Cost considerations factor into treatment planning. Individual session rates typically range from 80 to 150 Canadian dollars for sixty minutes, varying by location, therapist experience, and clinic setting. Many extended health insurance plans cover massage therapy, though coverage limits and requirements differ. Some practitioners offer package rates that reduce per-session costs. Individuals should verify their insurance benefits and discuss payment options with clinics before beginning treatment.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What aftercare practices support massage therapy benefits?
Proper aftercare extends therapeutic effects between sessions. Hydration helps flush metabolic waste released during massage, so drinking water after treatment supports this process. Applying heat through warm baths or heating pads can relax muscles and reduce post-massage soreness, while cold packs help with inflammation if present. Timing matters: heat generally works better for chronic tension, while cold suits acute flare-ups.
Gentle stretching maintains the flexibility gained during massage. Simple neck rolls, shoulder shrugs, and back extensions performed slowly and without force help preserve range of motion. Avoiding strenuous activity immediately after deep tissue work allows muscles to recover. Posture awareness throughout daily activities prevents tension from rebuilding. Ergonomic adjustments to workstations, regular movement breaks, and stress reduction techniques complement massage therapy for comprehensive relief.
Therapeutic massage offers a practical approach to managing neck, back, and shoulder tension when applied consistently and combined with self-care practices. Understanding different techniques, appropriate frequency, and aftercare strategies empowers individuals to use massage therapy effectively as part of their wellness plan. Qualified practitioners can assess individual needs and develop treatment approaches that address specific tension patterns while promoting overall wellbeing.




