Night Security in Italy – Understanding How Nighttime Safety, Patrols, and Facility Monitoring Are Organized
In Italy, night security operations ensure the protection of buildings and public spaces during evening and night hours. The industry follows well-defined processes, including monitoring systems, controlling access, patrolling, and coordinating with safety protocols. This overview helps understand the structure and typical practices in the night security sector without suggesting job opportunities.Italy’s approach to nighttime security reflects a combination of traditional patrol methods and modern technological solutions. Whether protecting commercial properties, residential complexes, industrial sites, or cultural landmarks, night security operations follow established protocols designed to minimize risk and maintain constant vigilance during vulnerable hours.
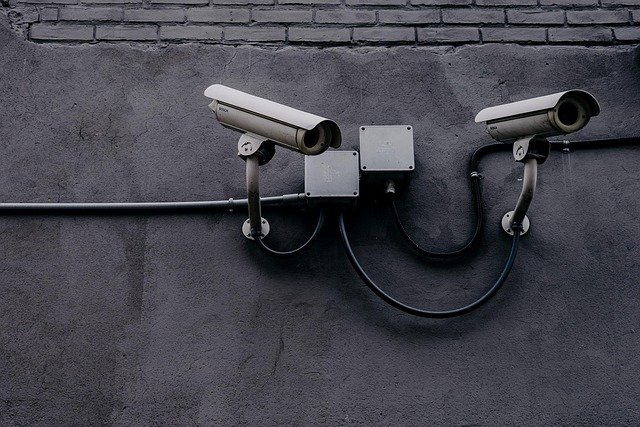

Italy’s approach to nighttime security combines traditional patrol methods with modern surveillance technology to ensure comprehensive protection of facilities during vulnerable overnight hours. The country’s security sector has evolved significantly, incorporating both human vigilance and technological innovation to address contemporary safety challenges. From historic city centers to sprawling industrial zones, nighttime security operations follow established protocols designed to deter criminal activity and respond swiftly to emergencies.
Night Security in Italy: Core Components and Structure
Nighttime security operations in Italy typically involve multiple layers of protection. Professional security officers conduct regular rounds throughout facilities, checking access points, monitoring alarm systems, and documenting any irregularities. These personnel often work in coordination with central monitoring stations that oversee multiple sites simultaneously. The organizational structure varies depending on facility type and size, but generally includes on-site guards, mobile patrol units, and remote surveillance operators. Security companies operating in Italy must comply with national regulations governing private security services, including licensing requirements and training standards for personnel.
Building Protection: Methods and Technologies Used
Protecting buildings during nighttime hours requires a combination of physical barriers, electronic systems, and human oversight. Modern facilities typically employ access control systems that restrict entry to authorized personnel, complemented by motion sensors and glass break detectors. Perimeter fencing with intrusion detection capabilities provides an initial defensive layer, while interior sensors monitor movement within secured zones. Security officers verify alarm activations and conduct visual inspections to distinguish between false alarms and genuine threats. Many Italian facilities have adopted integrated security management systems that consolidate video surveillance, access control, and alarm monitoring into unified platforms, allowing security personnel to respond more efficiently to incidents.
Patrol Routines: Systematic Approaches to Facility Monitoring
Structured patrol routines form the backbone of effective nighttime security. Security officers typically follow predetermined routes that cover all critical areas of a facility, with timing variations to prevent predictability. Modern patrol management often incorporates checkpoint scanning systems, where guards use RFID tags or QR codes at designated locations to verify completion of rounds. These digital systems generate timestamped records that supervisors can review to ensure compliance with patrol schedules. Patrol frequency varies based on risk assessment, with high-security facilities requiring more frequent rounds. Officers document observations in detailed logs, noting any unusual conditions, malfunctioning equipment, or security vulnerabilities discovered during their rounds.
Operational Standards and Training Requirements
Individuals working in nighttime security roles in Italy must meet specific qualification standards. Training programs cover topics including emergency response procedures, first aid, fire safety, conflict de-escalation, and legal aspects of security work. The Italian security sector operates under regulations that define minimum training hours and certification requirements for different security roles. Security personnel must understand their legal authority and limitations, as Italian law distinguishes between police powers and private security functions. Ongoing professional development ensures security officers remain current with evolving threats, new technologies, and updated protocols. Companies providing security services maintain quality standards through regular performance evaluations and supervisory oversight.
Technology Integration in Modern Security Operations
Contemporary nighttime security increasingly relies on technological solutions that enhance human capabilities. Video surveillance systems with night vision and motion detection provide continuous monitoring of extensive areas. Analytics software can identify unusual patterns or behaviors, alerting security personnel to potential issues before they escalate. Drone technology has begun appearing in security applications for large facilities, offering aerial perspectives during patrol operations. Communication systems enable instant coordination between on-site guards, mobile units, and central monitoring stations. However, technology serves as a complement rather than replacement for trained security personnel, whose judgment and adaptability remain essential for effective threat assessment and response.
Challenges and Considerations in Nighttime Security Work
Nighttime security operations present unique challenges that differ from daytime security requirements. Reduced visibility, lower staffing levels at protected facilities, and the psychological effects of overnight work schedules all influence operational effectiveness. Security personnel must maintain alertness during hours when human circadian rhythms naturally promote sleep, requiring companies to implement strategies that support officer wellness and performance. Environmental factors such as weather conditions can affect both patrol activities and equipment functionality. The isolated nature of nighttime security work also requires robust communication protocols and emergency backup procedures to ensure officer safety. Balancing comprehensive security coverage with operational costs remains an ongoing consideration for organizations managing security programs.
Coordination with Emergency Services and Authorities
Effective nighttime security operations in Italy involve established relationships with local law enforcement and emergency services. Security personnel serve as first responders to incidents occurring at protected facilities, assessing situations and contacting appropriate authorities when necessary. Clear protocols define when and how to escalate situations to police, fire services, or medical responders. Many security companies maintain direct communication channels with local police departments, facilitating rapid response to serious incidents. This coordination ensures that security operations complement rather than duplicate public safety services, creating an integrated approach to community protection during overnight hours.
Content Accuracy Note
This article is for informational purposes only and describes general practices within the security sector. Specific operational procedures, employment conditions, and requirements vary by company and location. Individuals interested in this field should conduct independent research and consult with licensed security service providers or relevant regulatory authorities for current information.